Version v1.8.0 Jan 12, 2024
1. Format Overview¶
1.1. Namespace – HDMF Common¶
Description: Common data structures provided by HDMF
Name: hdmf-common
Full Name: HDMF Common
Version: 1.8.0
- Authors:
Andrew Tritt
Oliver Ruebel
Ryan Ly
Ben Dichter
- Schema:
doc: base data types
source: base.yaml
title: Base data types
doc: data types for a column-based table
source: table.yaml
title: Table data types
doc: data types for different types of sparse matrices
source: sparse.yaml
title: Sparse data types
1.2. Type Hierarchy¶
2. Type Specifications¶
2.1. Base data types¶
base data types
2.1.1. Data¶
Overview: An abstract data type for a dataset.
Primitive Type: Dataset
Subtypes: ElementIdentifiers, VectorIndex, VectorData, DynamicTableRegion
Source filename: base.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.2.1
2.1.2. Container¶
Overview: An abstract data type for a group storing collections of data and metadata. Base type for all data and metadata containers.
Primitive Type: Group
Subtypes: SimpleMultiContainer, DynamicTable, AlignedDynamicTable, CSRMatrix
Source filename: base.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.2.2
2.1.3. SimpleMultiContainer¶
Overview: A simple Container for holding onto multiple containers.
SimpleMultiContainer extends Container and includes all elements of Container with the following additions or changes.
Extends: Container
Primitive Type: Group
Inherits from: Container
Source filename: base.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.2.3

Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<SimpleMultiContainer> |
Group |
Top level Group for <SimpleMultiContainer>
|
.<Data> |
Dataset |
Data objects held within this SimpleMultiContainer.
|
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<SimpleMultiContainer> |
Group |
Top level Group for <SimpleMultiContainer>
|
.<Container> |
Group |
Container objects held within this SimpleMultiContainer.
|
2.1.3.1. Groups: <Container>¶
Container objects held within this SimpleMultiContainer.
Extends: Container
Quantity: 0 or more
2.2. Table data types¶
data types for a column-based table
2.2.1. VectorData¶
Overview: An n-dimensional dataset representing a column of a DynamicTable. If used without an accompanying VectorIndex, first dimension is along the rows of the DynamicTable and each step along the first dimension is a cell of the larger table. VectorData can also be used to represent a ragged array if paired with a VectorIndex. This allows for storing arrays of varying length in a single cell of the DynamicTable by indexing into this VectorData. The first vector is at VectorData[0:VectorIndex[0]]. The second vector is at VectorData[VectorIndex[0]:VectorIndex[1]], and so on.
VectorData extends Data and includes all elements of Data with the following additions or changes.
Extends: Data
Primitive Type: Dataset
Dimensions: [[‘dim0’], [‘dim0’, ‘dim1’], [‘dim0’, ‘dim1’, ‘dim2’], [‘dim0’, ‘dim1’, ‘dim2’, ‘dim3’]]
Shape: [[None], [None, None], [None, None, None], [None, None, None, None]]
Inherits from: Data
Subtypes: VectorIndex, DynamicTableRegion
Source filename: table.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.3.1
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<VectorData> |
Dataset |
Top level Dataset for <VectorData>
|
.description |
Attribute |
Description of what these vectors represent.
|
2.2.2. VectorIndex¶
Overview: Used with VectorData to encode a ragged array. An array of indices into the first dimension of the target VectorData, and forming a map between the rows of a DynamicTable and the indices of the VectorData. The name of the VectorIndex is expected to be the name of the target VectorData object followed by “_index”.
VectorIndex extends VectorData and includes all elements of VectorData with the following additions or changes.
Extends: VectorData
Primitive Type: Dataset
Data Type: uint8
Dimensions: [‘num_rows’]
Shape: [None]
Inherits from: VectorData, Data
Source filename: table.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.3.2
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<VectorIndex> |
Dataset |
Top level Dataset for <VectorIndex>
|
.target |
Attribute |
Reference to the target dataset that this index applies to.
|
2.2.3. ElementIdentifiers¶
Overview: A list of unique identifiers for values within a dataset, e.g. rows of a DynamicTable.
ElementIdentifiers extends Data and includes all elements of Data with the following additions or changes.
Extends: Data
Primitive Type: Dataset
Data Type: int
Dimensions: [‘num_elements’]
Shape: [None]
Default Name: element_id
Inherits from: Data
Source filename: table.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.3.3
2.2.4. DynamicTableRegion¶
Overview: DynamicTableRegion provides a link from one table to an index or region of another. The table attribute is a link to another DynamicTable, indicating which table is referenced, and the data is int(s) indicating the row(s) (0-indexed) of the target array. DynamicTableRegion`s can be used to associate rows with repeated meta-data without data duplication. They can also be used to create hierarchical relationships between multiple `DynamicTable`s. `DynamicTableRegion objects may be paired with a VectorIndex object to create ragged references, so a single cell of a DynamicTable can reference many rows of another DynamicTable.
DynamicTableRegion extends VectorData and includes all elements of VectorData with the following additions or changes.
Extends: VectorData
Primitive Type: Dataset
Data Type: int
Dimensions: [‘num_rows’]
Shape: [None]
Inherits from: VectorData, Data
Source filename: table.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.3.4
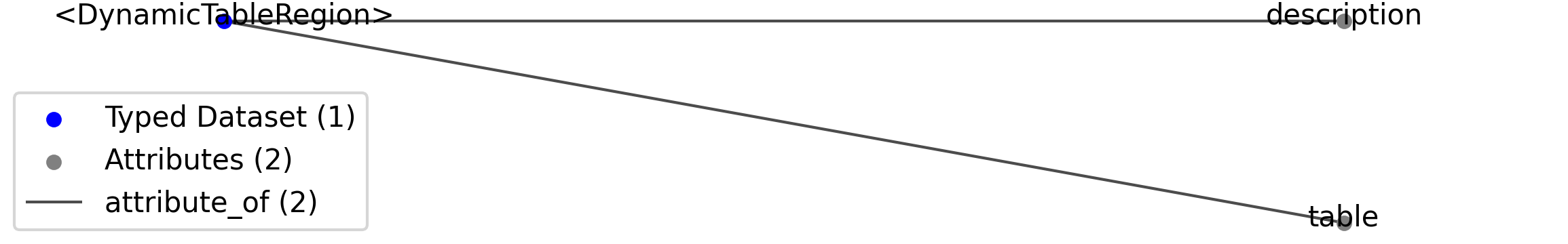
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<DynamicTableRegion> |
Dataset |
Top level Dataset for <DynamicTableRegion>
|
.table |
Attribute |
Reference to the DynamicTable object that this region applies to.
|
.description |
Attribute |
Description of what this table region points to.
|
2.2.5. DynamicTable¶
Overview: A group containing multiple datasets that are aligned on the first dimension (Currently, this requirement if left up to APIs to check and enforce). These datasets represent different columns in the table. Apart from a column that contains unique identifiers for each row, there are no other required datasets. Users are free to add any number of custom VectorData objects (columns) here. DynamicTable also supports ragged array columns, where each element can be of a different size. To add a ragged array column, use a VectorIndex type to index the corresponding VectorData type. See documentation for VectorData and VectorIndex for more details. Unlike a compound data type, which is analogous to storing an array-of-structs, a DynamicTable can be thought of as a struct-of-arrays. This provides an alternative structure to choose from when optimizing storage for anticipated access patterns. Additionally, this type provides a way of creating a table without having to define a compound type up front. Although this convenience may be attractive, users should think carefully about how data will be accessed. DynamicTable is more appropriate for column-centric access, whereas a dataset with a compound type would be more appropriate for row-centric access. Finally, data size should also be taken into account. For small tables, performance loss may be an acceptable trade-off for the flexibility of a DynamicTable.
DynamicTable extends Container and includes all elements of Container with the following additions or changes.
Extends: Container
Primitive Type: Group
Inherits from: Container
Subtypes: AlignedDynamicTable
Source filename: table.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.3.5
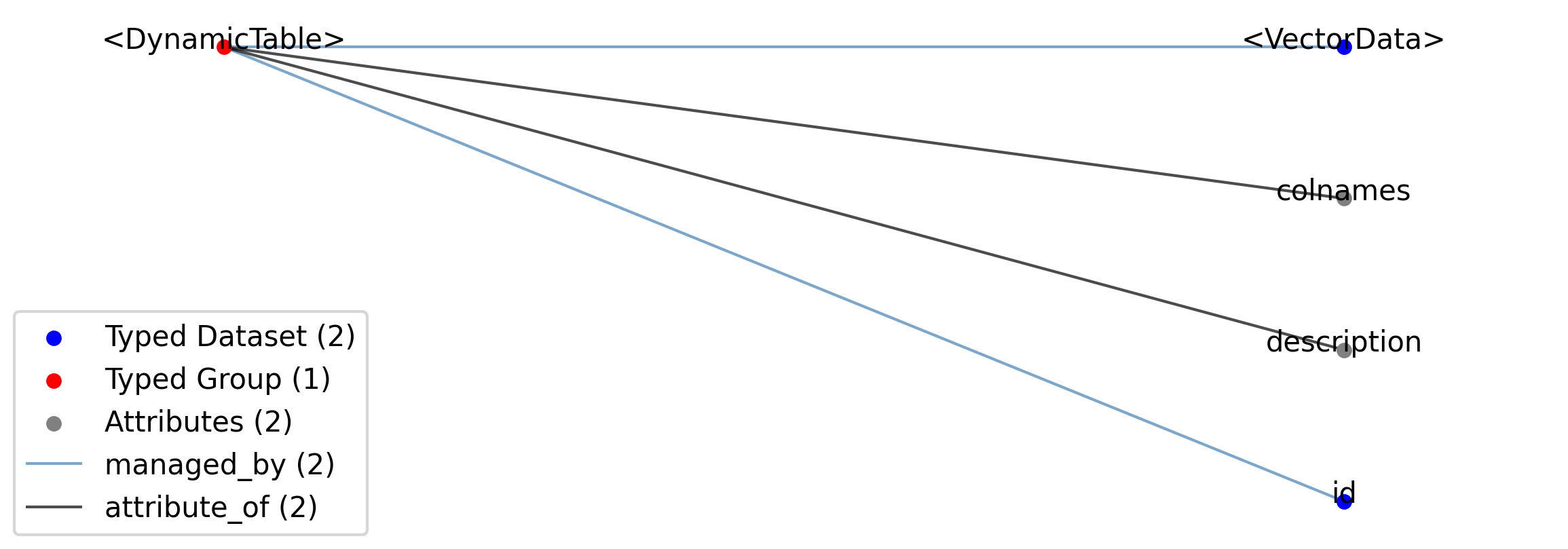
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<DynamicTable> |
Group |
Top level Group for <DynamicTable>
|
.colnames |
Attribute |
The names of the columns in this table. This should be used to specify an order to the columns.
|
.description |
Attribute |
Description of what is in this dynamic table.
|
.id |
Dataset |
Array of unique identifiers for the rows of this dynamic table.
|
.<VectorData> |
Dataset |
Vector columns, including index columns, of this dynamic table.
|
2.2.6. AlignedDynamicTable¶
Overview: DynamicTable container that supports storing a collection of sub-tables. Each sub-table is a DynamicTable itself that is aligned with the main table by row index. I.e., all DynamicTables stored in this group MUST have the same number of rows. This type effectively defines a 2-level table in which the main data is stored in the main table implemented by this type and additional columns of the table are grouped into categories, with each category being represented by a separate DynamicTable stored within the group.
AlignedDynamicTable extends DynamicTable and includes all elements of DynamicTable with the following additions or changes.
Extends: DynamicTable
Primitive Type: Group
Inherits from: DynamicTable, Container
Source filename: table.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.3.6
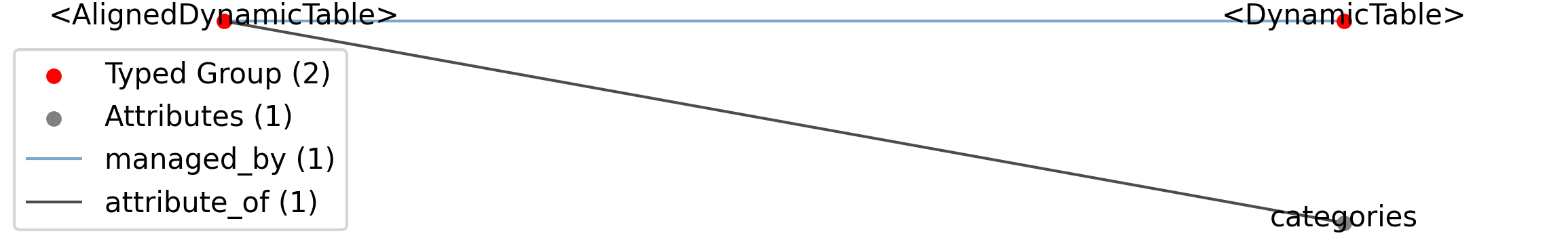
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<AlignedDynamicTable> |
Group |
Top level Group for <AlignedDynamicTable>
|
.categories |
Attribute |
The names of the categories in this AlignedDynamicTable. Each category is represented by one DynamicTable stored in the parent group. This attribute should be used to specify an order of categories and the category names must match the names of the corresponding DynamicTable in the group.
|
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<AlignedDynamicTable> |
Group |
Top level Group for <AlignedDynamicTable>
|
.<DynamicTable> |
Group |
A DynamicTable representing a particular category for columns in the AlignedDynamicTable parent container. The table MUST be aligned with (i.e., have the same number of rows) as all other DynamicTables stored in the AlignedDynamicTable parent container. The name of the category is given by the name of the DynamicTable and its description by the description attribute of the DynamicTable.
|
2.2.6.1. Groups: <DynamicTable>¶
A DynamicTable representing a particular category for columns in the AlignedDynamicTable parent container. The table MUST be aligned with (i.e., have the same number of rows) as all other DynamicTables stored in the AlignedDynamicTable parent container. The name of the category is given by the name of the DynamicTable and its description by the description attribute of the DynamicTable.
Extends: DynamicTable
Quantity: 0 or more
2.3. Sparse data types¶
data types for different types of sparse matrices
2.3.1. CSRMatrix¶
Overview: A compressed sparse row matrix. Data are stored in the standard CSR format, where column indices for row i are stored in indices[indptr[i]:indptr[i+1]] and their corresponding values are stored in data[indptr[i]:indptr[i+1]].
CSRMatrix extends Container and includes all elements of Container with the following additions or changes.
Extends: Container
Primitive Type: Group
Inherits from: Container
Source filename: sparse.yaml
Source Specification: see Section 3.4.1
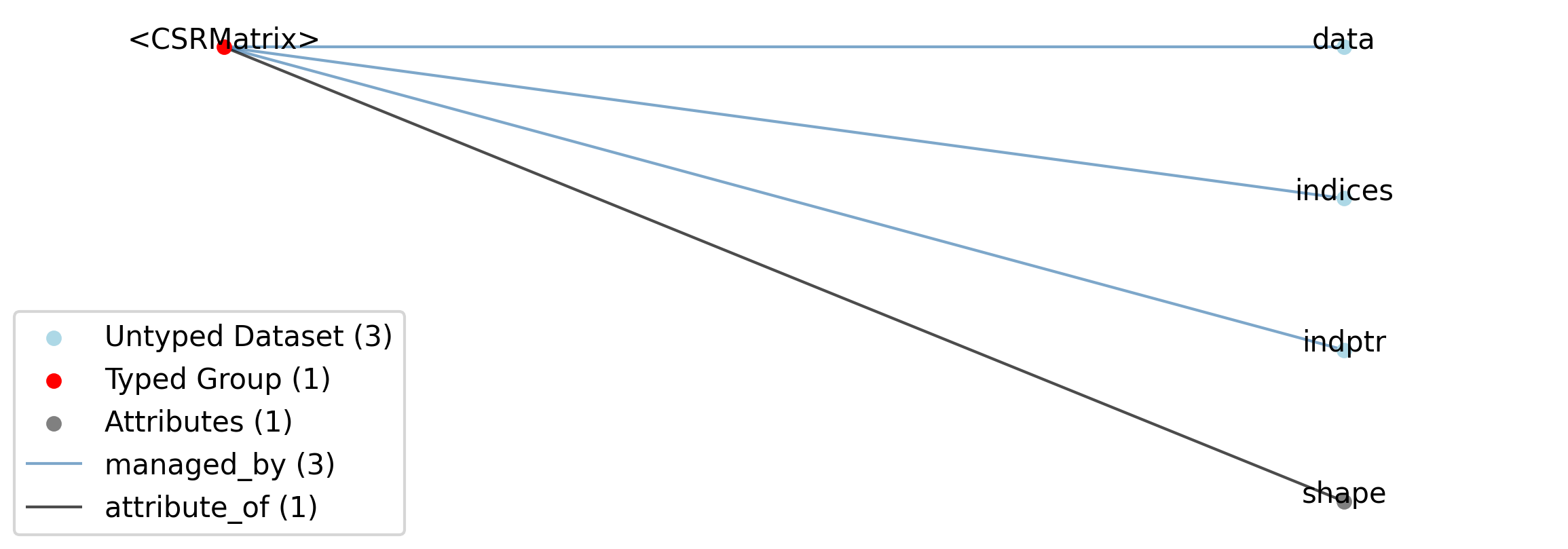
Id |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
<CSRMatrix> |
Group |
Top level Group for <CSRMatrix> |
.shape |
Attribute |
The shape (number of rows, number of columns) of this sparse matrix.
|
.indices |
Dataset |
The column indices.
|
.indptr |
Dataset |
The row index pointer.
|
.data |
Dataset |
The non-zero values in the matrix.
|
3. Schema Sources¶
Source Specification: see Section 3.1
3.1. Namespace – HDMF Common¶
Description: see Section 1.1
YAML Specification:
1author:
2- Andrew Tritt
3- Oliver Ruebel
4- Ryan Ly
5- Ben Dichter
6contact:
7- ajtritt@lbl.gov
8- oruebel@lbl.gov
9- rly@lbl.gov
10- bdichter@lbl.gov
11doc: Common data structures provided by HDMF
12full_name: HDMF Common
13name: hdmf-common
14schema:
15- doc: base data types
16 source: base.yaml
17 title: Base data types
18- doc: data types for a column-based table
19 source: table.yaml
20 title: Table data types
21- doc: data types for different types of sparse matrices
22 source: sparse.yaml
23 title: Sparse data types
24version: 1.8.0
3.2. Base data types¶
base data types
3.2.1. Data¶
Description: see Section 2.1.1
YAML Specification:
1data_type_def: Data
2doc: An abstract data type for a dataset.
3.2.2. Container¶
Description: see Section 2.1.2
YAML Specification:
1data_type_def: Container
2doc: An abstract data type for a group storing collections of data and metadata. Base
3 type for all data and metadata containers.
3.2.3. SimpleMultiContainer¶
Extends: Container
Description: see Section 2.1.3
YAML Specification:
1data_type_def: SimpleMultiContainer
2data_type_inc: Container
3datasets:
4- data_type_inc: Data
5 doc: Data objects held within this SimpleMultiContainer.
6 quantity: '*'
7doc: A simple Container for holding onto multiple containers.
8groups:
9- data_type_inc: Container
10 doc: Container objects held within this SimpleMultiContainer.
11 quantity: '*'
3.3. Table data types¶
data types for a column-based table
3.3.1. VectorData¶
Extends: Data
Description: see Section 2.2.1
YAML Specification:
1attributes:
2- doc: Description of what these vectors represent.
3 dtype: text
4 name: description
5data_type_def: VectorData
6data_type_inc: Data
7dims:
8- - dim0
9- - dim0
10 - dim1
11- - dim0
12 - dim1
13 - dim2
14- - dim0
15 - dim1
16 - dim2
17 - dim3
18doc: An n-dimensional dataset representing a column of a DynamicTable. If used without
19 an accompanying VectorIndex, first dimension is along the rows of the DynamicTable
20 and each step along the first dimension is a cell of the larger table. VectorData
21 can also be used to represent a ragged array if paired with a VectorIndex. This
22 allows for storing arrays of varying length in a single cell of the DynamicTable
23 by indexing into this VectorData. The first vector is at VectorData[0:VectorIndex[0]].
24 The second vector is at VectorData[VectorIndex[0]:VectorIndex[1]], and so on.
25shape:
26- -
27- -
28 -
29- -
30 -
31 -
32- -
33 -
34 -
35 -
3.3.2. VectorIndex¶
Extends: VectorData
Description: see Section 2.2.2
YAML Specification:
1attributes:
2- doc: Reference to the target dataset that this index applies to.
3 dtype:
4 reftype: object
5 target_type: VectorData
6 name: target
7data_type_def: VectorIndex
8data_type_inc: VectorData
9dims:
10- num_rows
11doc: Used with VectorData to encode a ragged array. An array of indices into the first
12 dimension of the target VectorData, and forming a map between the rows of a DynamicTable
13 and the indices of the VectorData. The name of the VectorIndex is expected to be
14 the name of the target VectorData object followed by "_index".
15dtype: uint8
16shape:
17-
3.3.3. ElementIdentifiers¶
Extends: Data
Description: see Section 2.2.3
YAML Specification:
1data_type_def: ElementIdentifiers
2data_type_inc: Data
3default_name: element_id
4dims:
5- num_elements
6doc: A list of unique identifiers for values within a dataset, e.g. rows of a DynamicTable.
7dtype: int
8shape:
9-
3.3.4. DynamicTableRegion¶
Extends: VectorData
Description: see Section 2.2.4
YAML Specification:
1attributes:
2- doc: Reference to the DynamicTable object that this region applies to.
3 dtype:
4 reftype: object
5 target_type: DynamicTable
6 name: table
7- doc: Description of what this table region points to.
8 dtype: text
9 name: description
10data_type_def: DynamicTableRegion
11data_type_inc: VectorData
12dims:
13- num_rows
14doc: DynamicTableRegion provides a link from one table to an index or region of another.
15 The `table` attribute is a link to another `DynamicTable`, indicating which table
16 is referenced, and the data is int(s) indicating the row(s) (0-indexed) of the target
17 array. `DynamicTableRegion`s can be used to associate rows with repeated meta-data
18 without data duplication. They can also be used to create hierarchical relationships
19 between multiple `DynamicTable`s. `DynamicTableRegion` objects may be paired with
20 a `VectorIndex` object to create ragged references, so a single cell of a `DynamicTable`
21 can reference many rows of another `DynamicTable`.
22dtype: int
23shape:
24-
3.3.5. DynamicTable¶
Extends: Container
Description: see Section 2.2.5
YAML Specification:
1attributes:
2- dims:
3 - num_columns
4 doc: The names of the columns in this table. This should be used to specify an order
5 to the columns.
6 dtype: text
7 name: colnames
8 shape:
9 -
10- doc: Description of what is in this dynamic table.
11 dtype: text
12 name: description
13data_type_def: DynamicTable
14data_type_inc: Container
15datasets:
16- data_type_inc: ElementIdentifiers
17 dims:
18 - num_rows
19 doc: Array of unique identifiers for the rows of this dynamic table.
20 dtype: int
21 name: id
22 shape:
23 -
24- data_type_inc: VectorData
25 doc: Vector columns, including index columns, of this dynamic table.
26 quantity: '*'
27doc: A group containing multiple datasets that are aligned on the first dimension
28 (Currently, this requirement if left up to APIs to check and enforce). These datasets
29 represent different columns in the table. Apart from a column that contains unique
30 identifiers for each row, there are no other required datasets. Users are free to
31 add any number of custom VectorData objects (columns) here. DynamicTable also supports
32 ragged array columns, where each element can be of a different size. To add a ragged
33 array column, use a VectorIndex type to index the corresponding VectorData type.
34 See documentation for VectorData and VectorIndex for more details. Unlike a compound
35 data type, which is analogous to storing an array-of-structs, a DynamicTable can
36 be thought of as a struct-of-arrays. This provides an alternative structure to choose
37 from when optimizing storage for anticipated access patterns. Additionally, this
38 type provides a way of creating a table without having to define a compound type
39 up front. Although this convenience may be attractive, users should think carefully
40 about how data will be accessed. DynamicTable is more appropriate for column-centric
41 access, whereas a dataset with a compound type would be more appropriate for row-centric
42 access. Finally, data size should also be taken into account. For small tables,
43 performance loss may be an acceptable trade-off for the flexibility of a DynamicTable.
3.3.6. AlignedDynamicTable¶
Extends: DynamicTable
Description: see Section 2.2.6
YAML Specification:
1attributes:
2- dims:
3 - num_categories
4 doc: The names of the categories in this AlignedDynamicTable. Each category is represented
5 by one DynamicTable stored in the parent group. This attribute should be used
6 to specify an order of categories and the category names must match the names
7 of the corresponding DynamicTable in the group.
8 dtype: text
9 name: categories
10 shape:
11 -
12data_type_def: AlignedDynamicTable
13data_type_inc: DynamicTable
14doc: DynamicTable container that supports storing a collection of sub-tables. Each
15 sub-table is a DynamicTable itself that is aligned with the main table by row index.
16 I.e., all DynamicTables stored in this group MUST have the same number of rows.
17 This type effectively defines a 2-level table in which the main data is stored in
18 the main table implemented by this type and additional columns of the table are
19 grouped into categories, with each category being represented by a separate DynamicTable
20 stored within the group.
21groups:
22- data_type_inc: DynamicTable
23 doc: A DynamicTable representing a particular category for columns in the AlignedDynamicTable
24 parent container. The table MUST be aligned with (i.e., have the same number of
25 rows) as all other DynamicTables stored in the AlignedDynamicTable parent container.
26 The name of the category is given by the name of the DynamicTable and its description
27 by the description attribute of the DynamicTable.
28 quantity: '*'
3.4. Sparse data types¶
data types for different types of sparse matrices
3.4.1. CSRMatrix¶
Extends: Container
Description: see Section 2.3.1
YAML Specification:
1attributes:
2- dims:
3 - number of rows, number of columns
4 doc: The shape (number of rows, number of columns) of this sparse matrix.
5 dtype: uint
6 name: shape
7 shape:
8 - 2
9data_type_def: CSRMatrix
10data_type_inc: Container
11datasets:
12- dims:
13 - number of non-zero values
14 doc: The column indices.
15 dtype: uint
16 name: indices
17 shape:
18 -
19- dims:
20 - number of rows in the matrix + 1
21 doc: The row index pointer.
22 dtype: uint
23 name: indptr
24 shape:
25 -
26- dims:
27 - number of non-zero values
28 doc: The non-zero values in the matrix.
29 name: data
30 shape:
31 -
32doc: A compressed sparse row matrix. Data are stored in the standard CSR format, where
33 column indices for row i are stored in indices[indptr[i]:indptr[i+1]] and their
34 corresponding values are stored in data[indptr[i]:indptr[i+1]].