1. Overview of hdmf-common¶
hdmf-common defines common data structures to be used across applications.
1.1. DynamicTable¶
The DynamicTable type is used to store tabular data. The tables are created in a columnar fashion
with each column stored in its own VectorData object. Rows of the table are assigned unique ids with
the required id column of type ElementIdentifier. The colnames attribute indicates the order of the columns.
1.2. VectorData¶
VectorData is the datatype used to store a column in a DynamicTable. If unpaired with a
VectorIndex object the first dimension is the row dimension, which must be the same across all of the columns in
that DynamicTable.
1.3. Ragged Arrays¶
(also known as Jagged Arrays)
Sometimes, you want to have a 2-d array where each row of the array has a different number of elements. For instance, in neuroscience, when storing the action potential times of sorted neurons, you might want to store them as a neuron x times matrix, but the problem is that each neuron will have a different number of spikes, so the second dimension will be inconsistent.
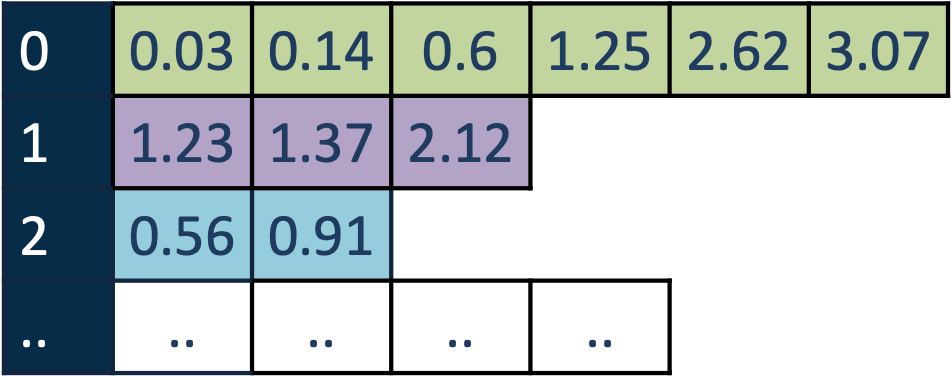
There are a number of possible solutions to this problem. Some solve it by NaN-padding
the array. You might want to store the spike times of each neuron in a separate dataset, but that will not scale well if
you have many neurons. In HDMF, you would store this using a pair of objects a VectorData and a VectorIndex
object. The VectorData array holds all of the data concatenated as a 1-d array, and it is paired with a link to a
VectorIndex object that indexes the data, forming a map between the rows of the ragged array and the indices of
VectorData.
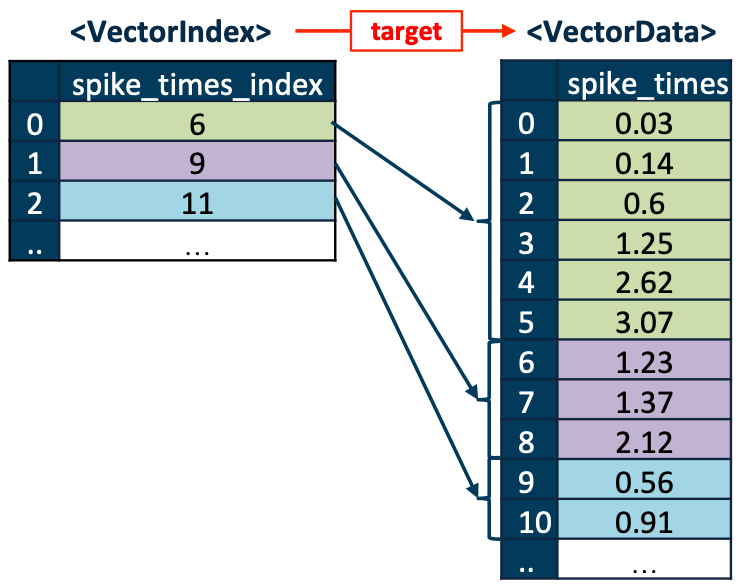
These objects are generally stored inside a DynamicTable, and the elements of VectorIndex map
onto the rows of the table. The VectorData object may be n-dimensional, but only the first dimension is ragged.
2. Experimental data structures¶
The following data structures are currently available under the HDMF-experimental schema. These are subject to change! They are not guaranteed to exist in the future nor maintain backward compatibility.
2.1. ExternalResources¶
The ExternalResources type is used to store references to data stored in external, web-accessible databases. This information is maintained using four row-based tables.